Sensorial education is a key aspect of the Montessori method of learning, which emphasises the development of the child's senses and the integration of sensory information. The Montessori approach is based on the belief that children are naturally curious and eager to learn, and that they absorb information most effectively through hands-on, sensory experiences.
In a Montessori classroom, children are introduced to a variety of materials that stimulate their senses, such as blocks, beads, and sound cylinders, which help them develop their sense of touch, sight, hearing, and other senses. These materials are designed to engage the child's attention and encourage them to explore and experiment on their own.
One of the key benefits of sensorial education is that it helps children understand and classify sensory information in a meaningful way. For example, children may learn to differentiate between different colors, shapes, and textures, which helps them develop their visual and tactile perception.
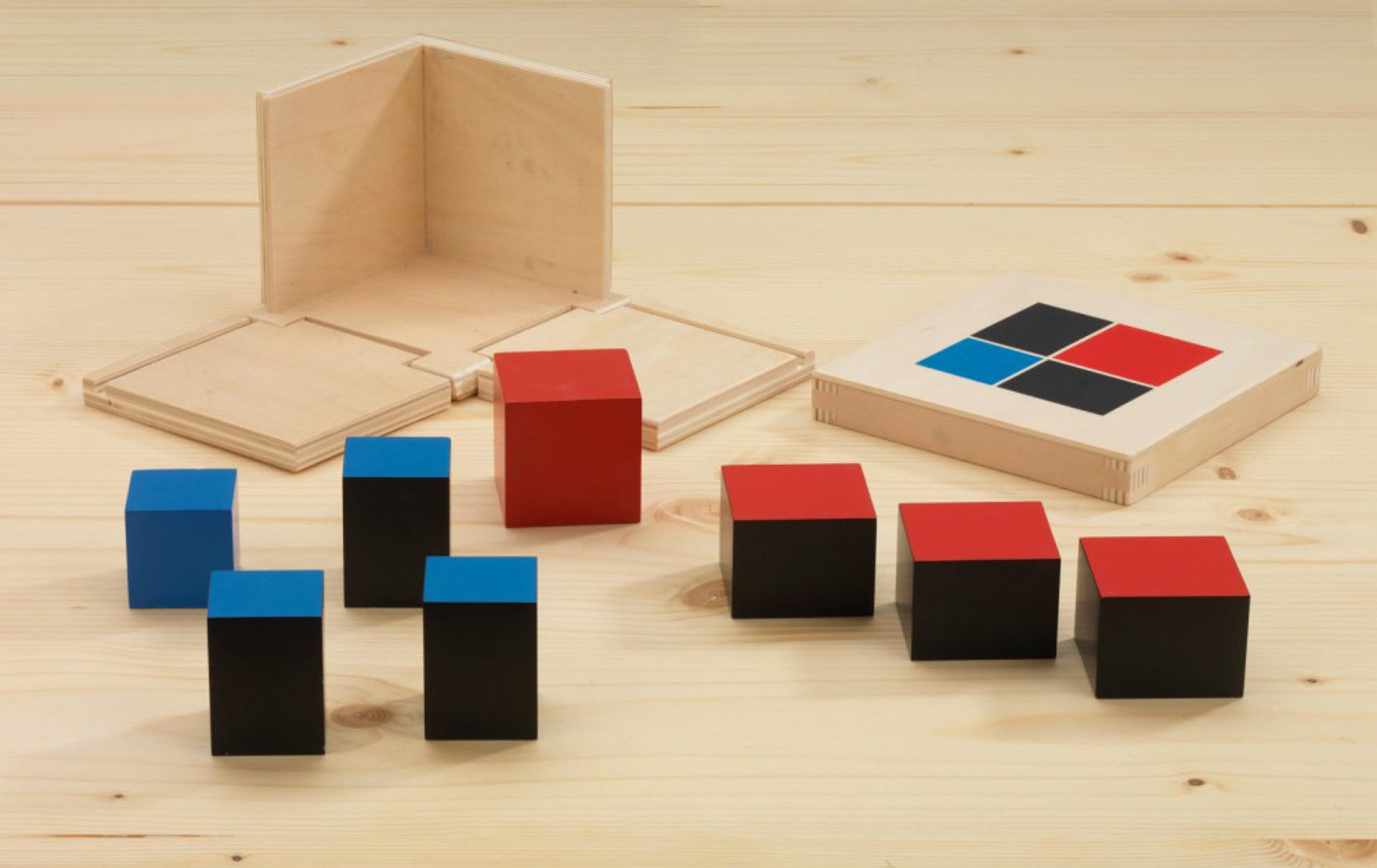

Another benefit is that it helps children develop their cognitive skills, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and memory. Children are encouraged to ask questions and make observations about the materials they are using, which helps them build their mental models of the world around them.
In addition, sensorial education also promotes self-confidence and independence in children. By giving them the freedom to explore and experiment on their own, children are encouraged to take ownership of their learning and develop a sense of pride and accomplishment in their achievements.
In conclusion, sensorial education is a critical aspect of the Montessori method, as it helps children develop their senses, cognitive skills, and self-confidence in a meaningful and engaging way. It is a great way to support a child's natural curiosity and love of learning, and provides a foundation for a lifetime of learning and exploration.